Introduction:
This empirical study investigates the impact of two distinct mathematical problem-solving methods – the Algebraic Formula Method and the Newton Sum Method – on enhancing ChatGPT's competence in effectively solving quadratic root functions. The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into mathematical problem-solving has paved the way for innovative approaches. In this study, we delve into the Algebraic Formula Method and the Newton Sum Method, essential techniques for solving quadratic root functions. We aim to showcase the profound influence of these methods on ChatGPT's capacity to excel in solving quadratic equations.
Evidence
Through concrete evidence, we demonstrate ChatGPT's adept utilization of the Newton Sum Method for quadratic root function calculations. While ChatGPT can compute quadratic root functions of the form using this method, its proficiency in using algebraic formula methods typically extends only up to . This marked discrepancy underscores the pivotal role that different methods play in amplifying the AI system's mathematical capabilities
Result
The results of this study provide concrete evidence of ChatGPT's superior utilization of the Newton Sum Method for calculating quadratic root functions. The model adeptly computes expressions of the form using this method, while its proficiency using algebraic formula methods is generally limited to . This striking discrepancy underscores the transformative impact that different methods can have on elevating the AI system's mathematical prowess.
Conclusion :
Pushing Boundaries: Pioneering Novel Maths Approaches for Overcoming Limitations in AI. This study serves as an illuminating testament to the significance of pioneering innovative methodologies, rules, theorems, or formulas to surmount the current limitations in AI systems like ChatGPT. These innovative pursuits hold the key to unlocking the untapped potential that lies within, propelling AI systems to greater heights of proficiency. In essence, they offer a strategic pathway towards expanding the capabilities of AI and pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved.
Discussion
The outcomes derived from this study underscore the significant influence wielded by the method selection in augmenting the mathematical competencies of ChatGPT. Particularly noteworthy is the application of the Newton Sum Method, which surfaces as a compelling exemplar. This method serves as a pivotal conduit through which the model surpasses its prior constraints, allowing it to venture into the realm of calculations entailing higher exponents.
Implications and Future Research:
These findings not only contribute to AI's mathematical competencies but also emphasize the need for pioneering new methods, rules, theorems, or formulas to further enhance AI systems like ChatGPT. Future research could explore the development of novel mathematical techniques tailored to AI systems, thus expanding their capabilities across diverse problem-solving domains.

 244 (Views)
244 (Views)  117 (Downloads)
117 (Downloads) 
 244 (Views)
244 (Views)  117 (Downloads)
117 (Downloads) 
 132 (Views)
132 (Views)  44 (Downloads)
44 (Downloads) 
 101 (Views)
101 (Views)  27 (Downloads)
27 (Downloads) 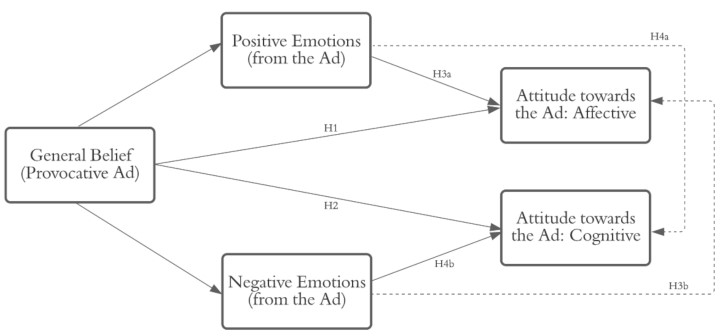
 617 (Views)
617 (Views)  305 (Downloads)
305 (Downloads) 
 1220 (Views)
1220 (Views)  294 (Downloads)
294 (Downloads) 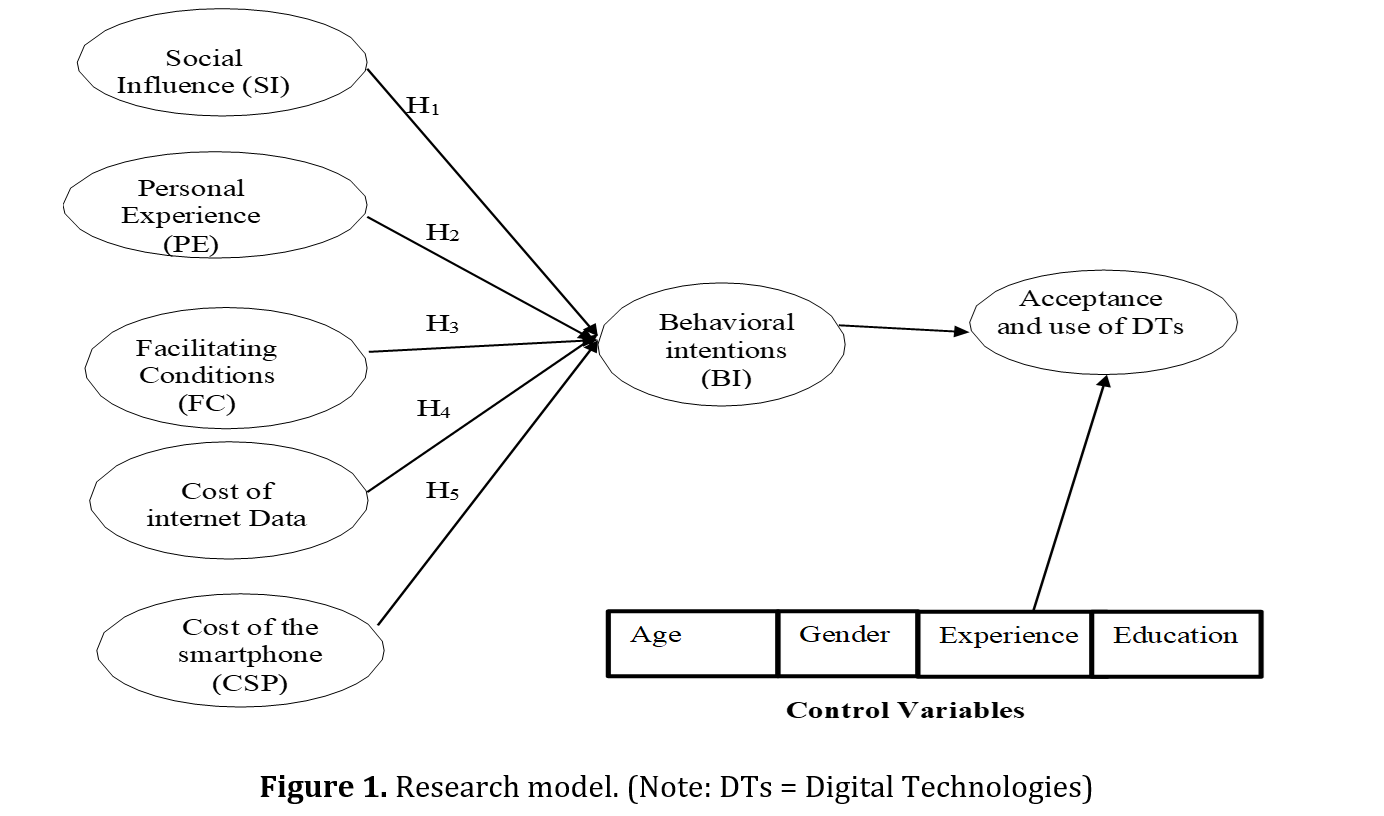
 433 (Views)
433 (Views)  222 (Downloads)
222 (Downloads)