Review
by Yakubu Bala Mohammed,
Mahmood Saidu Badara,
Hussaini Dan’azumi,
31 May 2024
Nowadays, cybersecurity stands out as a prominent topic frequently discussed by companies aiming to safeguard their data from hacking attempts. The rise of cyberspace has fuelled the expansion of electronic systems, creating a virtual digital realm that links computers and smartphones within the Internet of Things framework. Thus, the purpose of this study is to present the progress made thus far in applying AI-based intrusion detection systems (IDSs) to address cybercrimes, demonstrating their efficacy in detecting and preventing cyberattacks. The review utilized 4 scholarly databases; ScienceDirect, IEEE-Explore, Web of science, and Springer. 437 studies were extracted from the 4 chosen databases out of which only 54 studies were found to be relevant, thus included. The review found AI-based intrusion detection systems (IDSs) to be more robust and flexible compared to other conventional IDSs. Interestingly, the study results highlight how AI-based intrusion detection systems such as; ANN-based intrusion detection systems, agent-based intrusion detection systems, and Genetic-fuzzy intrusion detection systems, and other machine learning detection systems can be used to assist security experts in analyzing, designing, and developing security frameworks for combating cybercrimes. Lastly, the study proposed some areas for future studies.
 232 (Views)
232 (Views)  117 (Downloads)
117 (Downloads) 
 232 (Views)
232 (Views)  117 (Downloads)
117 (Downloads) 
 126 (Views)
126 (Views)  46 (Downloads)
46 (Downloads) 
 110 (Views)
110 (Views)  42 (Downloads)
42 (Downloads) 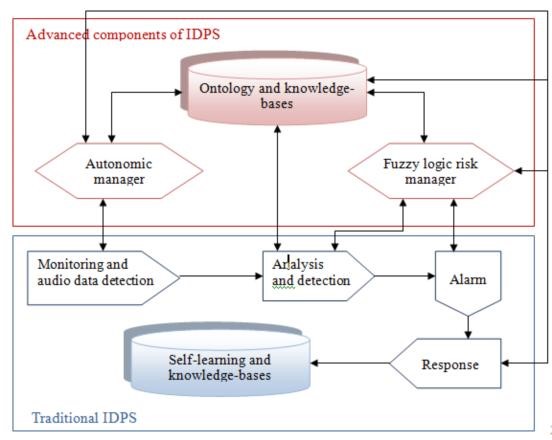
 116 (Views)
116 (Views)  98 (Downloads)
98 (Downloads) 
 2262 (Views)
2262 (Views)  1511 (Downloads)
1511 (Downloads) 
 328 (Views)
328 (Views)  109 (Downloads)
109 (Downloads)